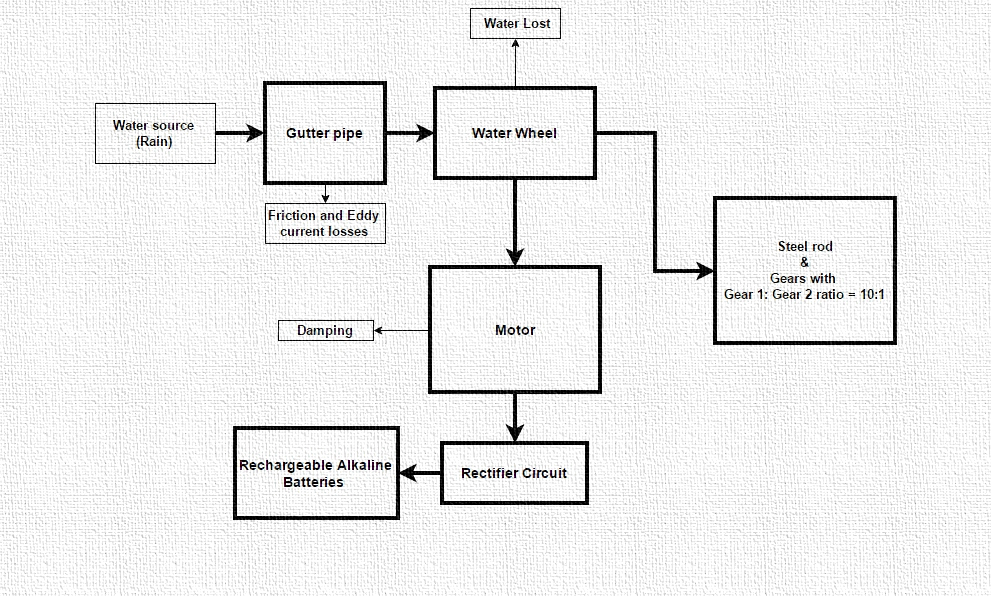
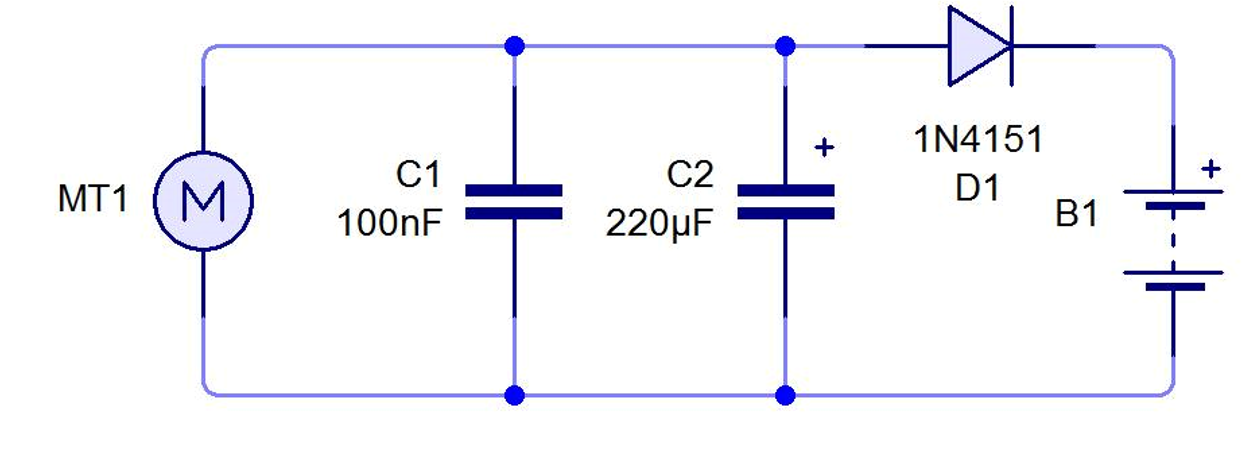
How does it work?
Conversion of Energy

As rainwater flows through the down pipe, it causes the water wheel to turn. At the top of the pipe, the water has gravitational potential energy. As it flows down, this energy is converted to mechanical energy as the wheel turns.
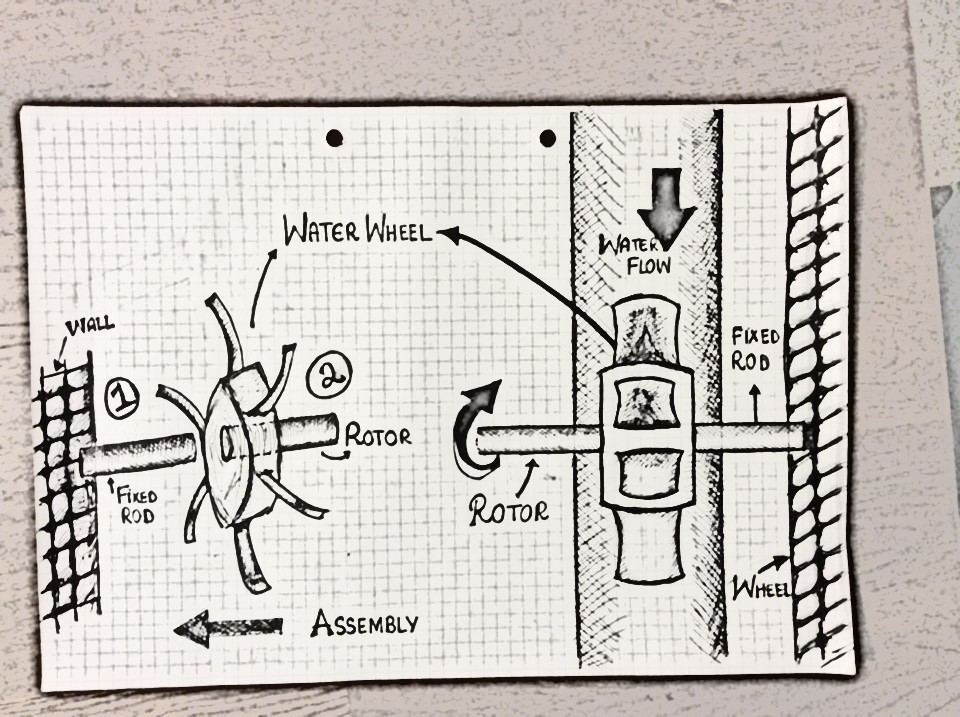
There is an axle attached to the wheel which turns when the wheel spins. The other side of the axle is connected to a dynamo which generates electricity when the axle causes it to turn. Mechanical energy is converted to electrical energy.